Sigmoidoscopy
Sigmoidoscopy is a test that uses a thin flexible tube with a camera at the end to look at the sigmoid colon (large intestine) for lesions including cancerous or pre-cancerous type. Sigmoid colon is the lower part of the large intestine that leads to rectum. A sigmoidoscopy may also be used to take a tissue sample or biopsy. Through sigmoidoscope, doctor is able to see any inflammation, bleeding or any other abnormality. If growth or other abnormalities are found during the procedure, the doctor may remove it.
How is a sigmoidoscopy performed?
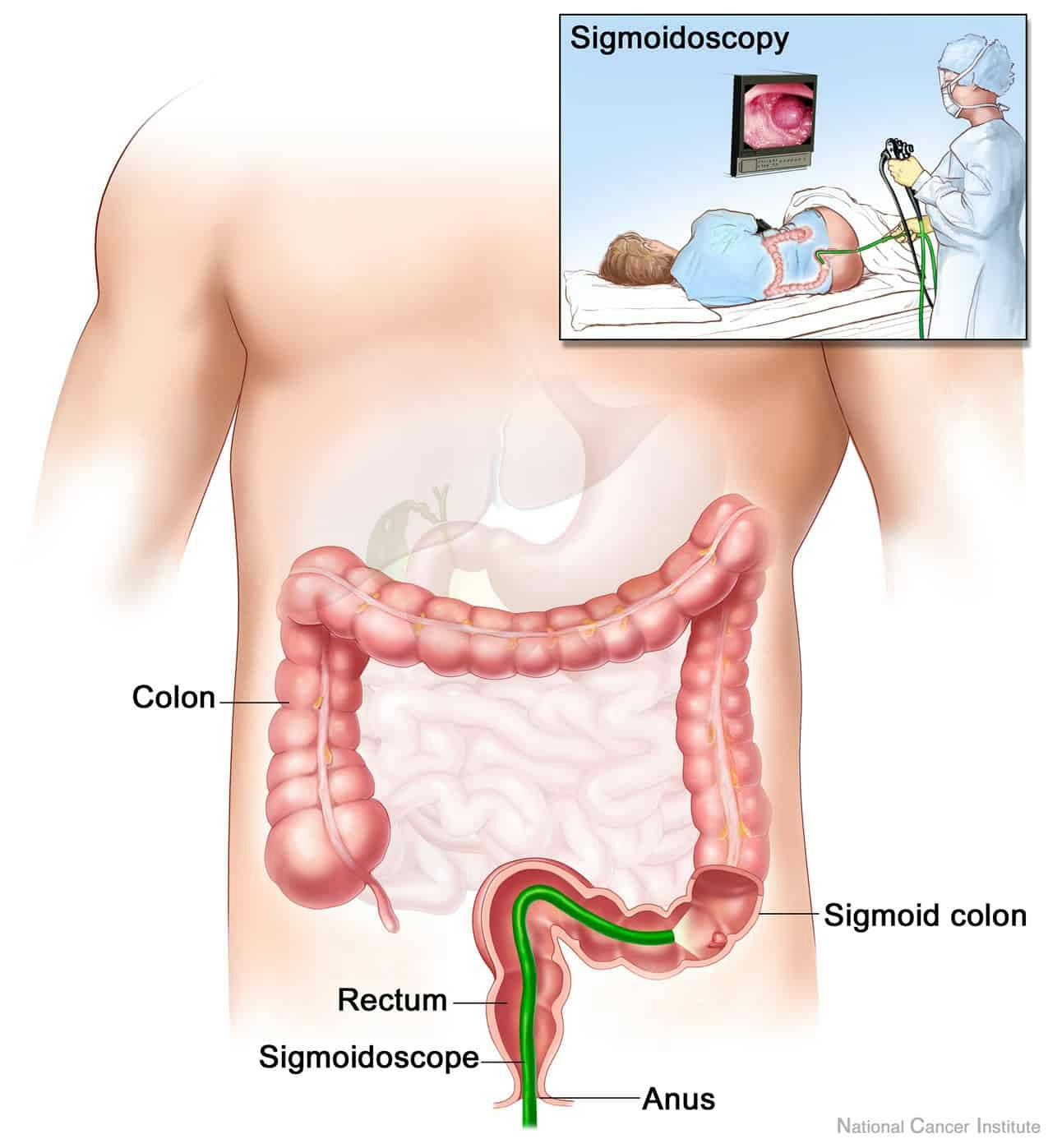
The procedure takes about 10-20 minutes and patients aren’t usually under sedation or anesthesia. The sigmoid colon and rectum need to be clean and empty before the test.
During a sigmoidoscopy, patient will be asked to lie on a table with the knees drawn up while the doctor inserts the sigmoidoscope into the anus, through the rectum, and into the lower part of colon. The doctor will use a small amount of air to expand the colon to see the colon walls. He can see the picture of the inside of the bowel on a TV monitor. The doctor may ask patient to move several times to adjust the scope for better viewing. Patient might feel discomfort or a strong urge to have a bowel movement. To lessen the cramps, patient may be advice to take several slow, deep breaths. If doctor finds polyps during sigmoidoscopy there is higher chance of having them elsewhere in colon so the doctor will recommend a colonoscopy to examine the rest of the colon.
During this procedure biopsies may be taken from the lining of the large intestine. The doctor will send the biopsy to the laboratory where a pathologist will examine it to find out if it is cancerous. Biopsy is usually required for the accurate diagnosis of the colon or rectal cancers. Once the doctor has seen the colon, the sigmoidoscope is slowly removed.
Preparation
For a sigmoidoscopy to work properly, it needs to have a clear view of the bowel. Therefore it is necessary that the colon is completely empty before the procedure. The healthcare provider will guide the patient on how to prepare the bowel for the test. Patient will be asked to follow a liquid diet for up to 24 hours before the exam. He/ she may be given laxatives (bowel cleanser), in order to ensure that everything is cleared out of the symptom. Some people also need to use an enema before bedtime. Enema is a liquid that is forced into the colon through the anus.
After procedure
Since sigmoidoscopy doesn’t require anesthesia, patient should be able to go home straight after the procedure. They can return to normal diet and routine right after sigmoidoscopy. Some people might feel bloated and have mild cramping after the test. This should go away after a few hours.
People often release gas that was put into the colon during the procedure. Some people may experience diarrhea while releasing the gas. Walking and moving around may help to ease pain.
If specimens were taken during the procedure they will be sent to the lab to check for cancer. The exam is considered negative if the doctor does not find any abnormalities. Depending on the findings, patient may need additional testing.
Why do doctors use sigmoidoscopy?
A sigmoidoscopy can help diagnose a variety of conditions including-
- Ulcers
- Polyps (small abnormal growth that may become cancerous)
- Colorectal cancer
- Diarrhea ( a loose watery stool that occurs more than three times a day)
- Constipation
- Hemorrhoids (swollen veins in the rectum and anus)
- Bleeding from anus
- Unexplained weight loss
What are the risks of a sigmoidoscopy?
Sigmoidoscopy is a very safe procedure. The side effects are temporary and may include:
- Pain: Patient may have some pain or cramping after the test, this usually passes quickly.
- Bleeding: If there was biopsy taken during the procedure, some amount of blood may appear in the stool. This usually stops on its own within a couple of days.
- Discomfort in the lower abdomen.
- In rare cases, a sigmoidoscope can make a tear in the colon or rectum wall. If this happens patient might need a surgery to correct it.
DISCLAIMER
This web page provides general information and discussions about health, medicine and related subjects. The information and other content provided on this website, or in any linked materials, are not intended and should not be construed as medical advice, nor is the information a substitute for professional medical expertise or treatment.
The content is for information purpose only and is not a medical advice. Qualified doctors have gathered information from reputable sources; however Credence Medicure Corporation is not responsible for errors or omissions in reporting or explanations. No individual should use the information, resources and tools contained herein to self diagnose or self treat any medical condition.
If you or any other person has a medical concern, you should consult with your health care provider or seek other professional medical treatment. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something that have read on this blog or in any linked materials. If you think you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor or emergency services immediately.
The opinions and views expressed on this blog and website have no relation to those of any academic, hospital, health practice or other institution. Credence Medicure Corporation gives no assurance or warranty regarding the accuracy, timeliness or applicability of the content.